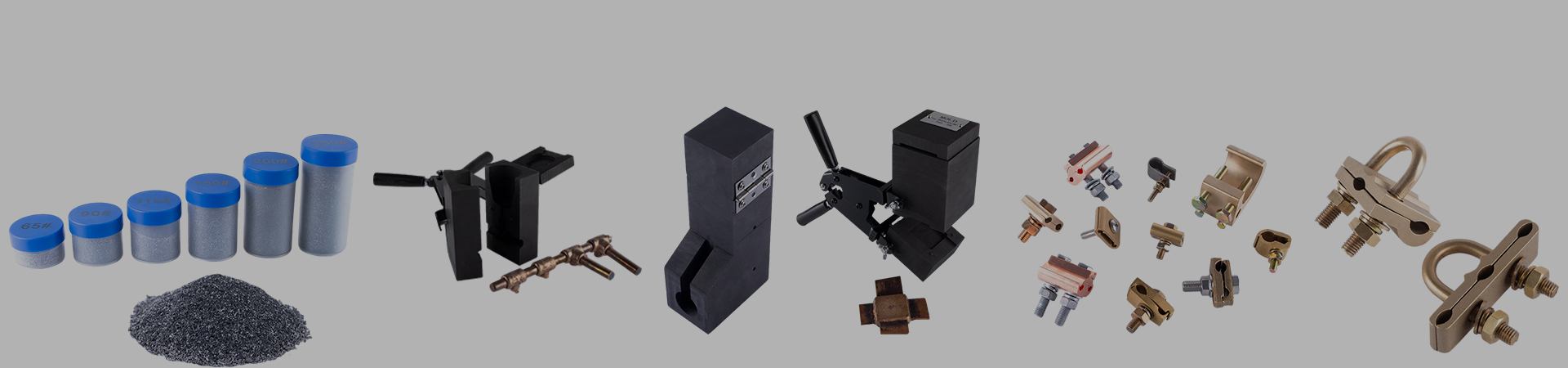
Mold Clamp Structural Design and Mechanical Performance Requirements
Functional load analysis forms the structural foundation of
Mold Clamp engineering and directly determines mechanical reliability during exothermic welding operations. A Mold Clamp is exposed to multiple interacting load types, including mechanical compression, localized shear, thermal expansion forces, and operational handling stress. These loads do not occur independently; instead, we observe overlapping stress states throughout the welding cycle. Shaoxing Sweld Electric Co., Ltd. integrates Mold Clamp load analysis into a broader manufacturing system that also includes exothermic welding powder, grounding components, and electrical connection hardware, allowing structural design to remain aligned with real application conditions. Mechanical clamping load represents the most visible force acting on a Mold Clamp. During mold closure, force must be applied evenly across the mold interface to maintain alignment and sealing integrity. Uneven force distribution causes localized gaps, leading to molten metal leakage or incomplete conductor fusion. To address this, load paths within the Mold Clamp structure are engineered to transmit force symmetrically from the tightening mechanism to the mold contact surfaces. By using CNC-machined structural components, Shaoxing Sweld Electric Co., Ltd. ensures dimensional accuracy that supports predictable force transmission during each operation cycle.
Thermal loads introduce additional complexity. During ignition, temperature gradients develop rapidly between the mold, Mold Clamp, and surrounding environment. Thermal expansion generates internal stress that interacts with mechanical preload. Mold Clamp structures must absorb this interaction without distortion or loss of clamping force. Our design approach avoids rigid overconstraint and instead allows controlled elastic response within defined regions of the clamp body. Operational handling loads must also be considered. Mold Clamps are frequently installed, removed, and repositioned in field environments. These actions introduce bending moments, impact forces, and off-axis stress. By incorporating sufficient structural stiffness and reinforced transition areas, Shaoxing Sweld Electric Co., Ltd. ensures Mold Clamps maintain structural integrity throughout repeated use without deformation accumulation.
Structural geometry optimization defines how effectively a Mold Clamp responds to applied loads, thermal expansion, and repeated use. Geometry governs stress distribution, stiffness, and fatigue resistance, making it a primary design variable in Mold Clamp engineering. Shaoxing Sweld Electric Co., Ltd. applies geometry optimization techniques across its Mold Clamp designs by leveraging real-time design feedback and CNC machining precision. The overall frame geometry of a Mold Clamp must balance strength and accessibility. Excessively bulky structures increase weight and reduce operational efficiency, while insufficient cross-sectional area leads to deformation under load. Our designs employ reinforced load-bearing sections positioned along principal force paths, ensuring mechanical strength is concentrated where required. Smooth transitions between structural sections reduce stress concentration and improve fatigue performance during repeated welding cycles.
Hinge and pivot geometry receive particular attention due to high stress exposure. Improper hinge alignment causes uneven rotation and accelerates wear. Precision-machined hinge axes ensure consistent rotational movement and stable mold closure. Shaoxing Sweld Electric Co., Ltd. maintains tight tolerance control in hinge components, supporting long-term alignment stability across large production volumes. Contact surface geometry also influences Mold Clamp performance. Flatness, parallelism, and surface alignment affect sealing pressure distribution. Minor geometric deviations can amplify during thermal expansion, resulting in localized separation. By integrating Mold Clamp production with exothermic welding mold manufacturing, dimensional compatibility is maintained across the entire system. Ergonomic geometry is considered during optimization. Mold Clamps must allow efficient manual operation while maintaining mechanical robustness. Structural geometry supports secure gripping, controlled tightening, and predictable release, reducing handling stress during installation and removal.
Material selection directly defines the mechanical behavior, durability, and thermal stability of a Mold Clamp. The operating environment of exothermic welding imposes demanding conditions that require materials capable of sustaining high mechanical loads and repeated thermal exposure. Shaoxing Sweld Electric Co., Ltd. aligns Mold Clamp material selection with its extensive experience in producing exothermic welding molds, grounding rods, and electrical hardware components. Mechanical strength is a primary requirement. Mold Clamp materials must maintain elastic behavior under maximum clamping force without yielding. Yield strength, tensile strength, and hardness are balanced to ensure structural reliability while avoiding brittleness. High-strength alloy steels are commonly selected to provide sufficient load-bearing capacity with controlled deformation characteristics.
Thermal resistance represents another essential consideration. During welding, Mold Clamps experience rapid heating followed by cooling, creating cyclic thermal stress. Materials must resist microstructural degradation caused by these cycles. Poor thermal stability results in loss of mechanical properties, dimensional drift, and reduced service life. By selecting materials with stable thermal expansion coefficients and fatigue resistance, long-term performance is maintained. Wear resistance is also critical, particularly at hinge points and contact interfaces. Repeated motion and load application generate frictional wear that accumulates over time. Material hardness and surface treatment options are evaluated to reduce wear rates while preserving machinability. Shaoxing Sweld Electric Co., Ltd. applies standardized material verification procedures to ensure consistency across production batches. Compatibility with CNC machining processes is another requirement. Materials must support precision machining without excessive tool wear or dimensional instability. This compatibility enables high-volume production with reliable quality control, supporting the company’s daily production capacity for exothermic welding molds and related accessories.
Precision machining and dimensional control define whether Mold Clamp structural design can be reliably translated from engineering intent into consistent physical products. Even well-designed Mold Clamp geometry fails to perform if dimensional accuracy is not maintained across production. For this reason, machining precision is treated as a structural performance variable rather than a downstream manufacturing concern. Shaoxing Sweld Electric Co., Ltd. integrates Mold Clamp machining into a broader CNC-based production system that also supports exothermic welding molds, grounding components, and electrical hardware, allowing unified tolerance control across related products. Dimensional control begins with critical interface surfaces. Mold Clamp contact areas must align precisely with mold surfaces to ensure uniform clamping pressure. Deviations in flatness or parallelism lead to localized pressure concentration, accelerating mold wear and increasing leakage risk during molten metal flow. Through multi-axis CNC machining centers, Shaoxing Sweld Electric Co., Ltd. maintains controlled surface geometry that supports predictable force distribution under operational loads.
Tolerance management is equally important in hinge assemblies and force-transmission components. Excessive clearance results in lost motion and unstable clamping force, while overly tight fits increase friction and wear. Precision machining allows hinge pins, slots, and mating components to maintain functional clearances that remain stable throughout repeated thermal cycles. Our production environment supports tight dimensional repeatability, enabling Mold Clamps to behave consistently across large production batches. Surface finish quality also influences mechanical behavior. Rough or irregular surfaces increase friction, promote wear, and interfere with smooth operation. Controlled machining parameters and post-machining finishing processes are applied to ensure contact surfaces exhibit stable friction characteristics. This consistency reduces variability during field use and improves long-term performance. Real-time manufacturing feedback further enhances dimensional control. By integrating design adjustments directly into CNC programming, Shaoxing Sweld Electric Co., Ltd. ensures Mold Clamp geometry can be optimized quickly in response to production data, supporting efficient customization and continuous structural refinement.
Structural durability under repeated operational cycles represents a defining performance requirement for Mold Clamp products. Unlike single-use components, Mold Clamps are expected to perform reliably across numerous welding operations, often in demanding field environments. Each cycle introduces mechanical loading, thermal expansion, cooling contraction, and handling stress. Over time, these factors interact to influence fatigue behavior, wear progression, and dimensional stability. Shaoxing Sweld Electric Co., Ltd. accounts for these cumulative effects during Mold Clamp structural design and manufacturing. Fatigue resistance forms the core of durability analysis. Repeated application of clamping force generates cyclic stress within structural members, particularly near transitions, hinge roots, and force application points. Structural geometry is optimized to reduce sharp corners and abrupt section changes that amplify stress concentration. Gradual transitions and reinforced load paths help distribute stress more evenly, extending fatigue life.
Thermal cycling further influences durability. Each welding operation exposes the Mold Clamp to elevated temperatures followed by cooling, producing expansion and contraction that interact with mechanical stress. Materials and structural features must tolerate this behavior without progressive deformation. By aligning Mold Clamp design with extensive experience in exothermic welding mold production, Shaoxing Sweld Electric Co., Ltd. ensures thermal behavior remains compatible across the system. Wear accumulation is another durability consideration. Hinge points, sliding interfaces, and contact surfaces experience friction during each operation. Structural design minimizes unnecessary relative motion while maintaining functional flexibility. In high-wear regions, structural reinforcement and surface treatments are used to slow degradation. This approach reduces maintenance frequency and extends usable service life. Structural stiffness and reinforced connection zones ensure resistance to accidental drops or off-axis loading. Through controlled machining and material selection, Shaoxing Sweld Electric Co., Ltd. ensures Mold Clamps maintain dimensional integrity despite repeated handling and operational cycles.


 English
English 








