What is hot-dip galvanized round steel?
Hot-dip galvanized round steel, also known as hot-dip galvanized round bar or galvanized steel rod, is a type of carbon steel bar with a circular cross-section that has been coated with a thick layer of zinc through the hot-dip galvanizing process. This protective zinc coating forms a strong metallurgical bond with the steel surface, creating long-term resistance against rust and corrosion. Because of its excellent durability, mechanical strength, and low maintenance requirements, hot-dip galvanized round steel is widely used in outdoor, underground, and high-humidity environments.
The base material is typically made from mild or medium carbon steel such as Q235, Q355, ASTM A36, or similar structural grades. After forming and rolling into round bars, the steel undergoes a galvanizing treatment. During this process, the bars are immersed in molten zinc at approximately 450°C–460°C. Unlike paint or electroplating, which only create a thin surface film, hot-dip galvanizing produces multiple alloy layers that chemically bond zinc and iron together. This bond ensures that the coating will not easily peel or flake off, even under mechanical stress or impact.
The zinc coating provides dual protection. First, it acts as a physical barrier that prevents water, oxygen, and chemicals from reaching the steel surface. Second, zinc offers sacrificial protection, meaning that even if the coating is scratched, the surrounding zinc will corrode first to protect the exposed steel. This self-protective behavior significantly extends the service life of the product.
Because of these advantages, hot-dip galvanized round steel is commonly used in construction frameworks, power transmission structures, grounding and earthing systems, lightning protection networks, fencing posts, and infrastructure projects. Especially in electrical grounding systems, round steel is preferred due to its good conductivity, high strength, and easy installation.
For example, in professional grounding and lightning protection projects, galvanized round steel is often connected with ground rods, stranded grounding wires, and exothermic welding connections to form a stable, low-resistance earthing system. This ensures long-term electrical safety and corrosion resistance even when buried underground.
What is the hot-dip galvanizing process for round steel bars?
The hot-dip galvanizing process for round steel bars is a carefully controlled surface treatment method designed to create a thick, durable, and permanently bonded zinc coating on the steel surface. This process ensures maximum corrosion resistance and long-term performance, making it far superior to painting or electro-galvanizing for outdoor or underground applications.
The process typically consists of several key stages:
Degreasing: First, the round steel bars are cleaned to remove oil, grease, and dirt from the surface. Contaminants can prevent proper zinc adhesion, so thorough cleaning is critical for coating quality.
Pickling: After degreasing, the bars are immersed in an acid solution, usually hydrochloric or sulfuric acid. This step removes rust, mill scale, and oxides from the steel surface, exposing fresh metal and preparing it for galvanizing.
Fluxing: Next, the steel is dipped into a flux solution (commonly zinc ammonium chloride). Fluxing prevents oxidation before galvanizing and improves the wetting reaction between molten zinc and steel.
Hot-Dip Galvanizing: The prepared round bars are then submerged into a molten zinc bath at around 450–460°C. During immersion, zinc reacts with iron to form several zinc-iron alloy layers (Gamma, Delta, Zeta layers) topped with a pure zinc layer. This metallurgical bond makes the coating extremely strong and resistant to peeling.
Cooling and Inspection: After galvanizing, the bars are withdrawn, cooled in air or water, and inspected for coating thickness, uniformity, and surface quality. Excess zinc is removed to ensure smoothness and proper dimensions.
The resulting coating thickness usually ranges from 50 to 100 microns or more, depending on the steel chemistry and immersion time. This thick coating provides decades of protection even in harsh environments.
For grounding and lightning protection systems, proper galvanizing is particularly important because corrosion at connection points can increase electrical resistance. Therefore, many projects combine galvanized round steel with permanent connection technologies such as exothermic welding. This creates a molecular bond between conductors, ensuring both electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance throughout the system’s lifespan.
What is the corrosion resistance of hot-dip galvanized round steel?
Hot-dip galvanized round steel is well known for its excellent corrosion resistance and long service life, which makes it one of the most reliable materials for outdoor, underground, and harsh industrial environments. Thanks to the thick zinc coating formed during the hot-dip galvanizing process, the steel can remain protected for decades with little or no maintenance.
The corrosion resistance mainly comes from two mechanisms:
Barrier protection
The zinc layer isolates the steel from moisture, oxygen, salt, and chemicals, preventing direct contact between the environment and the base metal.
Sacrificial (cathodic) protection
Zinc is more chemically active than iron. When the coating is damaged, zinc corrodes first and protects the exposed steel. This “self-healing” effect significantly reduces rust formation.
Typical service life by environment:
- Indoor or dry areas → 50+ years
- Urban outdoor areas → 30–40 years
- Coastal/marine areas → 20–30 years
- Heavy industrial zones → 10–20 years
In many grounding and earthing projects, galvanized round steel is buried directly in soil. In these cases, corrosion resistance is especially critical because rust increases electrical resistance and reduces system safety. A properly galvanized round bar with 80–100 μm coating can maintain stable performance underground for decades.
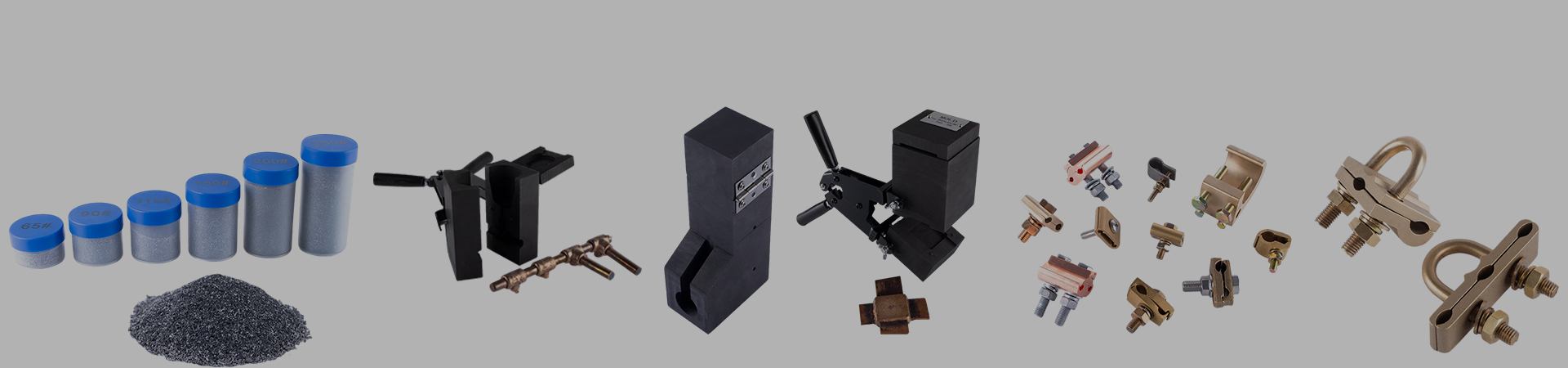
This is why professional grounding solution providers often select hot-dip galvanized round steel together with reliable connection methods. For instance, Shaoxing Sweld Electric Co., Ltd., established in 2018 in Shaoxing, China, specializes in complete grounding and lightning protection systems. Shaoxing Sweld Electric Co., Ltd. supplies exothermic welding powder, ground rods, ground wires, stranded wires, and electrical hardware connectors. By combining galvanized round steel with permanent exothermic welding connections, the entire grounding network achieves low resistance, strong bonding, and superior corrosion resistance.
With ISO9001, ISO14001, and ISO45001 certifications and an annual production capacity of 500 tons of exothermic welding powder, Shaoxing Sweld Electric Co., Ltd. provides long-lasting and safe solutions for power, construction, and lightning protection projects. This integrated approach ensures that galvanized round steel components can deliver stable performance for 30–50 years or more in real-world applications.


 English
English 








